
In the world of global politics, only few people are as interesting and influential as Vladimir Putin. Despite the presence of Joe Biden and Xi Jinping, leaders of two powerful nations, Putin stands out as the most powerful person in the world. For over twenty years, he has not only guided Russia but also played a key role in international affairs. With a background as a KGB agent, his clever strategies, strong determination, and mysterious character have left a lasting impact.
Even in the face of the Ukraine war and the severe sanctions imposed by the international community, Putin’s influence remains unmatched. Remarkably, Russia is riding the wave of the fastest-growing economy in Europe, surpassing many despite the economic pressures. As we explore his rise to power, his main tactics, and his effect on world events, we uncover the many layers of a leader whose power reaches far beyond Russia’s borders.
Table of Contents
Early life and Journey of Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin was born on October 7, 1952, in Leningrad, now known as Saint Petersburg, Russia. His father, Vladimir Spiridonovich Putin, was a conscript in the Soviet Navy, serving in the submarine fleet in the early 1930s. His mother, Maria Shelomova, was a factory worker. Growing up in post-war Leningrad, Putin’s early life was marked by the hardships of the time.
Despite these challenges, Putin was determined and ambitious from a young age. He pursued martial arts, particularly judo, and became proficient, earning a black belt. Academically, he was also driven, eventually graduating from Leningrad State University in 1975 with a degree in law.


Headquarters, Moscow
During his university years Putin joined the KGB in 1975, the main security agency for the Soviet Union. Putin’s intelligence career spanned over 16 years, during which he gained valuable experience in espionage and international relations. One notable assignment took him to Dresden, East Germany, where he served undercover until the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989. This experience abroad sharpened his strategic thinking and understanding of global politics.
Putin resigned from the KGB in 1991 as the Soviet Union was collapsing, and he transitioned into politics. He quickly rose through the political ranks, becoming the head of the Federal Security Service (FSB) and later Prime Minister of Russia. In 1999, amid political and economic turmoil, President Boris Yeltsin appointed Putin as Acting President. On December 31, 1999, Yeltsin resigned, and Putin became the President of Russia.
Putin won his first official presidential election in 2000 and was re-elected in 2004. Due to the constitutional limit of two consecutive terms, he became Prime Minister in 2008 while Dmitry Medvedev served as President. This move was strategically designed to maintain Putin’s control over Russian politics, with Medvedev positioned to protect and secure Putin’s influence. In 2012, Putin was re-elected as President and has remained a dominant figure in Russian and global politics since then, winning subsequent elections in 2018.
Comparison with other most powerful persons in the world
Vladimir Putin’s role as a global leader is often compared to that of Joe Biden, President of the United States, and Xi Jinping, President of China. Despite leading powerful nations with significant military and economic capabilities, the nature of their power and their ability to take decisive action differ markedly.

Joe Biden:
As the leader of the United States, the most powerful nation in terms of economic and military strength, Joe Biden holds a significant position on the world stage. However, Biden’s power is constrained by the democratic processes of the country. Major decisions, particularly those involving military action or significant policy changes, require approval and discussion within Congress. This system of checks and balances ensures that no single individual holds absolute power, which can sometimes lead to slower decision-making processes. Biden’s ability to act unilaterally is limited compared to Putin, who can make rapid, decisive moves without needing parliamentary consent.
Xi Jingping:
Xi Jinping, as the leader of China, wields considerable authority similar to Putin’s centralised control. Under Xi’s leadership, China has asserted itself aggressively on the global stage, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. However, Xi faces challenges in maintaining relationships with other nations. The growing distrust from countries like India and other ASEAN nations has put pressure on China’s international standing. Furthermore, China’s economy, while robust, is heavily dependent on its global trade relationships. Any significant diplomatic fallout could risk economic instability, forcing Xi to navigate a careful balance between assertive policies and maintaining international trust.
Vladimir Putin:
In contrast, Vladimir Putin’s leadership style is characterised by a high degree of autonomy and centralised power. Unlike Biden, Putin does not require parliamentary approval for his actions, allowing him to act swiftly and decisively on both domestic and international fronts. This capability was evident in his bold moves such as the annexation of Crimea and the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, which drew severe international sanctions. Despite these sanctions, Putin has managed to sustain and even bolster Russia’s economy, making it one of the fastest-growing in Europe. Russia, under Putin, faces fewer diplomatic constraints compared to China. With fewer dependencies on global trade relationships, Putin can afford to take risks that leaders like Xi Jinping cannot.
Moreover Putin has an estimated net worth of more than $200 billion. World’s richest man Elon Musk also said in an interview that Putin is significantly richer than him.
NATO and Ukraine War
The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) was set up on April 4, 1949, to stand against the Soviet Union and keep its member countries safe. Its mutual defence rule (Article 5) says that an attack on one member is an attack on all, which helps prevent attacks on NATO countries.
NATO has grown a lot since it started and wants to expand more in order to limit Russia. It consists most of the European countries like France, Germany, UK, Italy, Turkey, Spain etc along with U.S. and Canada. NATO’s growth, especially into former Eastern Bloc countries like Finland and Ukraine, has made Russia feel threatened.
Russia’s worries grew with NATO placing missiles and nuclear weapons in countries near its borders. The idea of Ukraine joining NATO made Russia even more anxious because of its important location.Things got worse when Russia took over Crimea in 2014. In 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine, saying it was necessary to protect its security and stop NATO from getting closer to its borders.The conflict led to fast and strong economic penalties on Russia by many countries around the world.
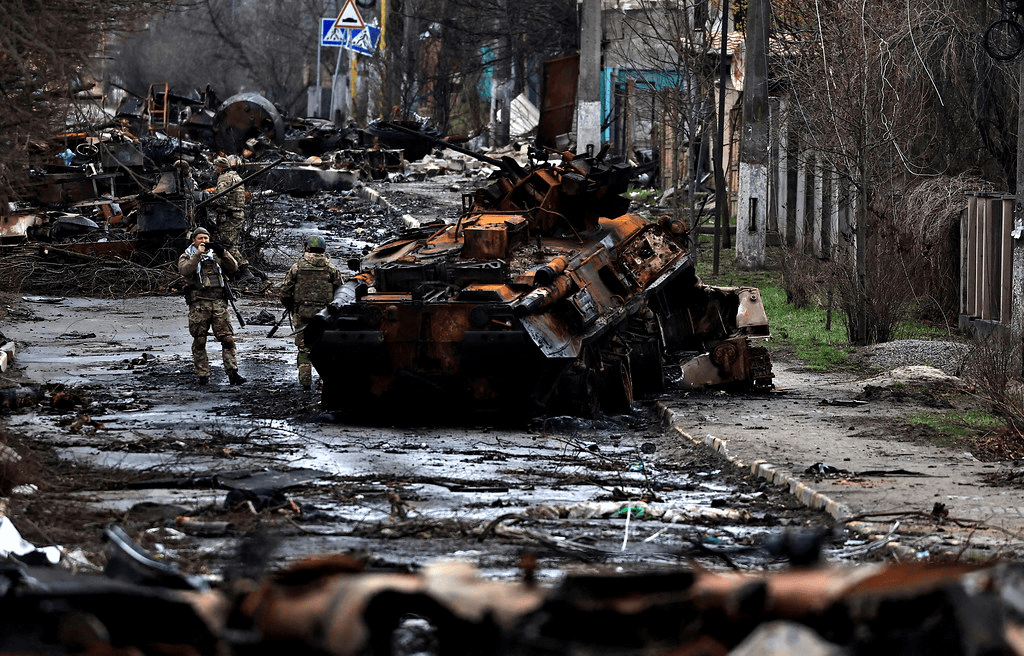

These penalties targeted Russian banks, energy companies, and important people. One of the most significant sanctions was Russia’s removal from the SWIFT international payments system. This action aimed to cut off Russian banks from the global financial network, making it very hard for them to do business internationally. Additionally, European countries imposed an oil embargo, banning the import of Russian oil. This aimed to weaken Russia’s economy, as oil exports are a major source of revenue for the country. The goal was to make Russia change its actions, and find a peaceful solution to the conflict.
Despite these penalties and worldwide disapproval, Russia kept up its military actions in Ukraine. The United States and other NATO countries have given Ukraine powerful weapons and military help, turning the conflict into a proxy war. However, Russia has managed to gain a lot of land in Ukraine, showing its strong military power.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has expressed willingness for peace but set conditions, including Russia leaving all occupied areas of Ukraine, including Crimea. However, Russian President Vladimir Putin has made it clear that he will never accept these conditions.

President of Ukraine
Amid these tensions, there are reports of Russia planning “Operation Unthinkable,” which allegedly involves destroying France’s (and UK’s) nuclear weapons. The idea is to diminish the risk of these weapons being provided to Ukraine, which could then use them in the Ukraine-Russia war. Additionally, if Russia ever tries to invade Europe, European countries would not have these nuclear weapons to use against Russia.
This plan further escalates the conflict and shows Russia’s readiness to confront NATO countries directly. Making such bold decisions and facing NATO alone is not easy, which underscores Putin’s power. His ability to take these actions and maintain a strong position against a major alliance like NATO highlights his significant influence on the global stage.
Russia’s Military and technological accomplishments
Tsar Bomba
Russia holds the record for detonating the most powerful nuclear bomb ever, demonstrating its formidable nuclear capabilities.
(Energy released by Tsar Bomba = 50,000 Kilotons of TNT, which is equivalent of 1570x times the combined energy of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bombs)
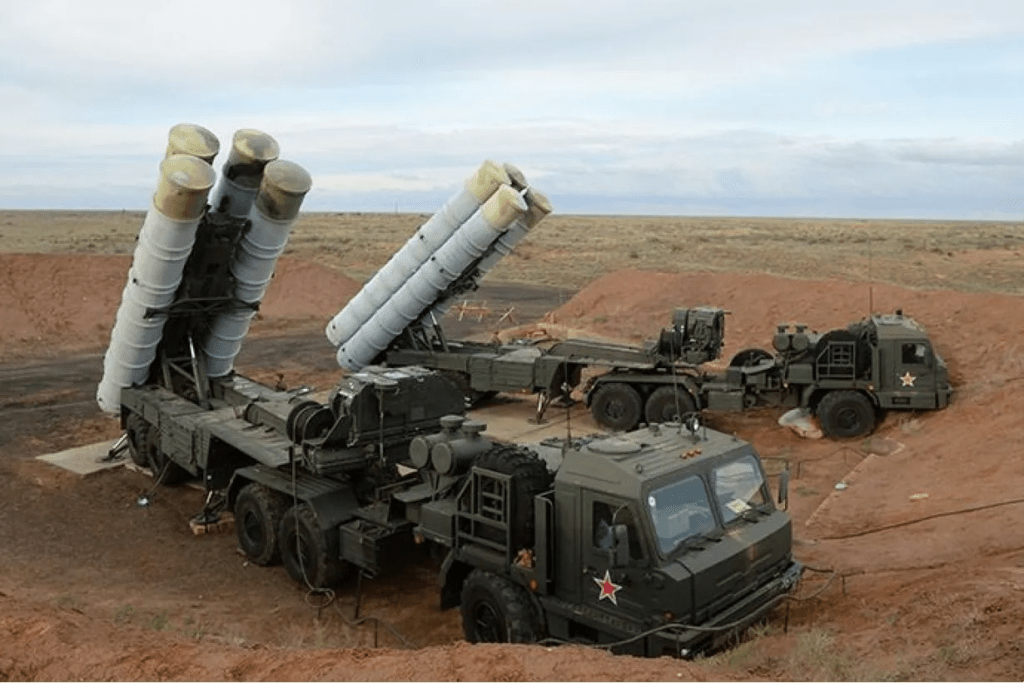


S-500 Air Defence System
It is the world’s best air defence system which can destroy intercontinental as well as hypersonic cruise missiles and aircraft. It showcases Russia’s cutting-edge defence capabilities.
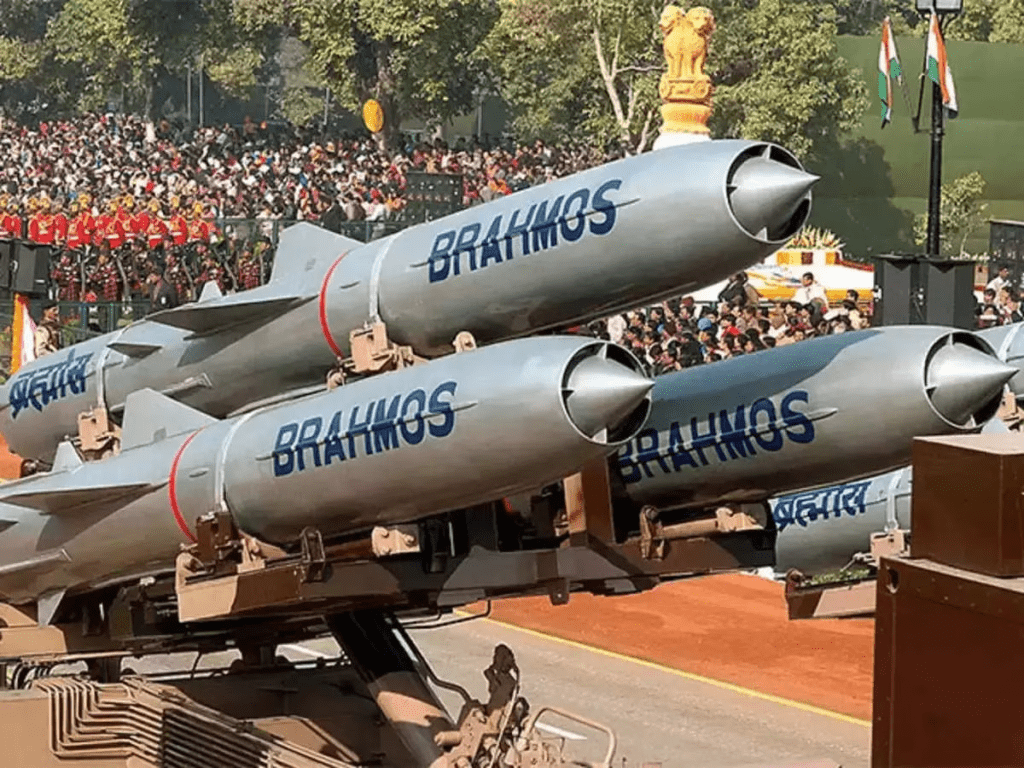
BrahMos Missile
Developed in partnership with India, it is the most advanced cruise missile which is celebrated for its unmatched speed and precision in missile technology.
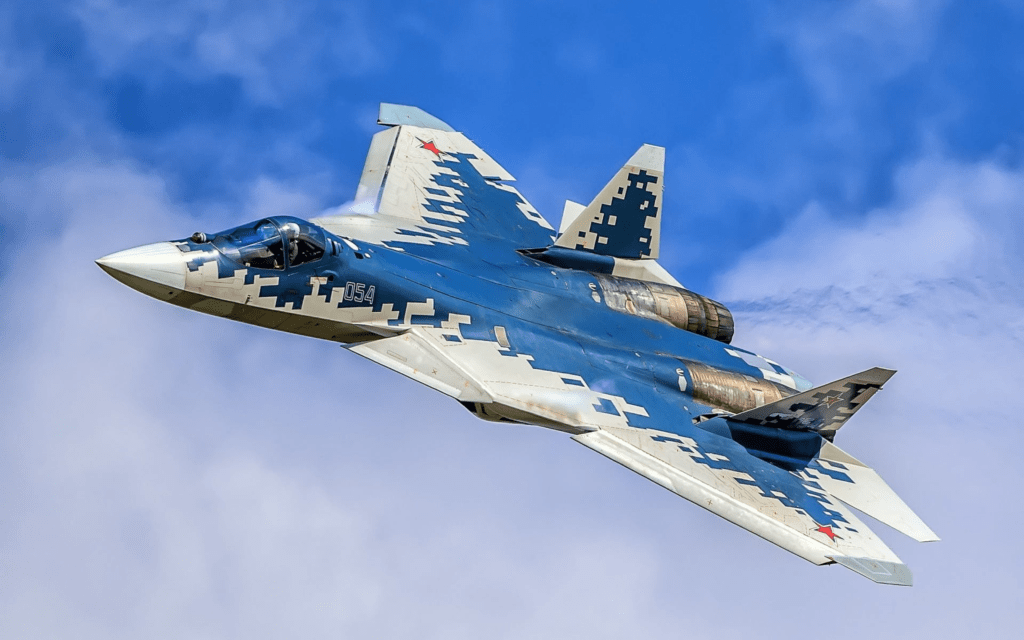
Su-57 Fighter Jet
Russia’s Su-57 fighter jet, a 5th-generation aircraft, ranks among the world’s top fighters and competes with U.S. made F-22 Raptor, highlighting Russia’s leadership in aviation technology.
Russia has the world’s second strongest defence system after USA. It demonstrates extensive military capabilities on a global scale. Nuclear Submarines Integrated with advanced portable nuclear power plants, Russia’s nuclear submarines exemplify its innovation in naval defence and energy technology. You can read our article on Nuclear Energy as well.


NASA’s Collaboration Since the Cold War, NASA has relied on Russian technology, including critical aerospace components, highlighting Russia’s pivotal role in international aerospace cooperation.
Throughout history, Russia’s military resilience, particularly in pivotal battles like the defence of Stalingrad during World War II and against Napoleon’s invasion, underscores its steadfast commitment to national defence.
These achievements are a testament to Russia’s enduring strength under President Vladimir Putin’s strategic leadership, shaping its formidable position in global military and technological arenas and ultimately making him the strongest being on the planet.
Geopolitical Achievements
Impact as an Oil Exporter
Being a significant oil exporter, Russia wields influence over global oil prices, impacting economies worldwide. Russia has strategically exported oil to China and India at discounted rates, often trading in gold, INR, or Chinese currency despite Western sanctions.
Economic Resilience Despite Sanctions
Despite sanctions following the Ukraine conflict, Russia has managed to sustain and even grow its economy faster than many European countries.
Shift Towards China, North Korea, and India
As the USA and European countries seeks to isolate Russia geopolitically, Russia has strengthened ties with China, North Korea, and India, fostering trade and military cooperation.
Role in BRICS Alliance. Russia plays a pivotal role within BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa), an alliance challenging Western dominance, with discussions ongoing about introducing a new BRICS currency.
Military Alliances and partnerships
Recent military pacts include an agreement with North Korea, promising mutual defence in case of aggression, showcasing Russia’s strategic alliances beyond traditional Western partnerships. It has good military ties with China as well who supports each other with weapons and in United Nations voting. India has granted Russia military access to ports and facilities, deepening bilateral defence ties and regional strategic cooperation.
Assertive Military Actions
Russia’s positioning of nuclear submarines near the USA serves as a warning against American involvement in Ukraine, signalling readiness to defend its interests and deter external intervention.
Failures and weakness
Threats of Direct Involvement and Land Issues
Russia faces the threat of direct involvement from countries like France amid ongoing conflicts, while unresolved territorial disputes with Japan and China remain a concern.
Dependency on China
Russia’s significant economic and strategic dependency on China poses challenges, influencing its geopolitical decisions and alliances.
Importance of Public Support
Maintaining public support within Russia is crucial for sustaining political stability and leadership credibility, particularly in the face of domestic challenges and international pressures.
Prolonged Ukraine Conflict
Putin’s expectation of a swift resolution to the Ukraine conflict has not materialised, with the conflict ongoing for over two years, posing diplomatic and military challenges.
Internal Separatist Movements
Internal challenges include separatist movements in various regions of Russia, demanding independence and posing internal security threats.
Impact of Sanctions
Sanctions from Western nations have resulted in economic losses, including the banning of European and American companies from operating in Russia, exacerbating dependency on Indo-Pacific markets.
Conclusion
After taking into consideration his supreme military power over the world’s second strongest nation with such advanced weapons and rich mineral resources, supreme leader of a country with most number of nuclear weapons which is more than 5500, personal net worth being one of the highest in the world, having superpower allies like China, having literally no opposition in his country against him, we can conclude that Putin is currently the most powerful person in the world.
Looking ahead, Vladimir Putin’s future remains pivotal in shaping global dynamics. His strategic acumen and resilience have positioned Russia prominently despite international challenges. As Putin navigates internal complexities and global pressures, including sanctions and regional conflicts, his leadership will continue to influence geopolitical balances.
